Poverty in India – Breaking the Chains
India has achieved what many considered impossible just a decade ago—lifting 171 million people out of extreme poverty while simultaneously reducing multidimensional poverty by 61.3%. This remarkable transformation represents one of the fastest large-country poverty reductions in modern history, fundamentally rewriting the narrative of global poverty alleviation.
The story of breaking poverty’s chains in India is not just about numbers—it’s about 269 million lives transformed, 24.82 crore people escaping multidimensional deprivation, and a nation proving that targeted interventions, technological innovation, and political will can create miracles at scale.
The Magnitude of Transformation: Numbers That Tell a Story
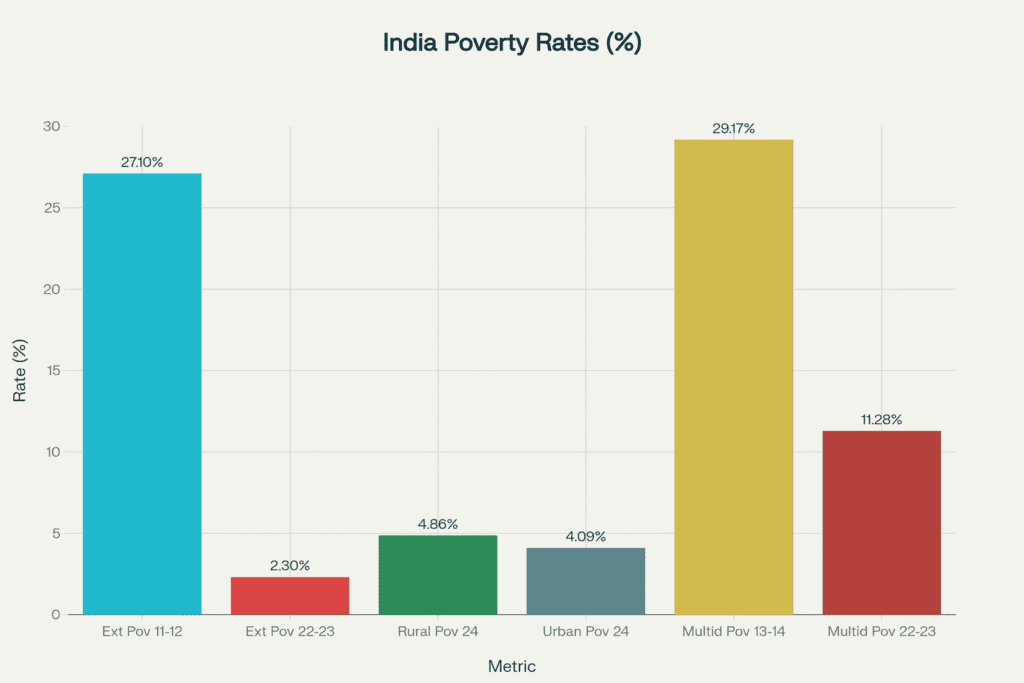
India Poverty Rate Change: Comparison from 2011-12 to 2024 across multiple metrics
India’s poverty landscape has undergone a dramatic metamorphosis that deserves global recognition. The extreme poverty rate plummeted from 27.1% in 2011-12 to just 2.3% in 2022-23—a staggering 91.5% reduction. Even more impressive, rural poverty dropped from 25.7% to 4.86%, while urban poverty fell to 4.09%.visionias+4
Key Poverty Reduction Statistics:
| Poverty Metric | Before | After | Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extreme Poverty Rate | 27.1% (2011-12) | 2.3% (2022-23) | 91.5% |
| Rural Poverty | 25.7% (2011-12) | 4.86% (2024) | 81.1% |
| Urban Poverty | 13.7% (2011-12) | 4.09% (2024) | 70.1% |
| Multidimensional Poverty | 29.17% (2013-14) | 11.28% (2022-23) | 61.3% |
| Overall Current Poverty | 21.9% (2011-12) | 4-4.5% (2024) | 78.5% |
This transformation becomes even more remarkable when viewed through the lens of purchasing power parity. The World Bank’s updated poverty line of $3 per day shows only 5.75% of Indians now live in extreme poverty, compared to 27% in 2011-12.visionias+1
State Champions: Leading the Poverty Elimination Drive
The poverty reduction success story varies dramatically across states, with some achieving extraordinary results that deserve individual recognition. Five key states—Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Bihar, West Bengal, and Madhya Pradesh—accounted for 65% of India’s extreme poor in 2011-12 but contributed to two-thirds of the overall decline by 2022-23. developmentaid
Top Performing States in Poverty Reduction:
- Uttar Pradesh: 60 million people lifted from extreme poverty
- Bihar: 37.7 million people escaped poverty
- Madhya Pradesh: 23 million people transformed
- Rajasthan: 18.7 million people empowered
- Maharashtra: 15.2 million people elevated
The success in these traditionally impoverished states demonstrates that targeted interventions can work even in the most challenging contexts. Uttar Pradesh alone, with 5.94 crore people escaping multidimensional poverty, showcases how political commitment combined with effective implementation can achieve scale.pib+1
The Arsenal of Change: Government Schemes That Worked
India’s poverty reduction success rests on a comprehensive ecosystem of targeted interventions that address multiple dimensions of deprivation simultaneously. These schemes don’t operate in isolation—they create synergistic effects that amplify their individual impacts.
Major Poverty Alleviation Schemes and Their Reach:
Food Security and Nutrition
- PM Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana: 800 million people receive free food grains, extended until December 2028pmfias+1
- Antyodaya Anna Yojana: Subsidized food for the poorest households
- Mid-Day Meal Programs: Nutritional security for children
Employment and Livelihood
- MGNREGA: Guarantees 100 days of employment to rural households, creating 216.32 crore person-days of work ecoholics+1
- National Rural Livelihood Mission: 85 million households covered through self-help groups ispp
- Skill Development Programs: PMKVY training for market-relevant skills drishtiias+1
Financial Inclusion Revolution
- PM Jan Dhan Yojana: 550 million bank accounts opened, bringing the unbanked into formal financial systems indianarrative+1
- Direct Benefit Transfer: ₹3.48 lakh crore saved by eliminating leakagesIndianarrative
- PM Kisan: ₹6000 annual income support to 14 crore farmers pmfias
Housing and Infrastructure
- PM Awas Yojana: 2 crore affordable houses constructed ecoholics+1
- Ujjwala Yojana: 95 million LPG connections providing clean cooking fuel cleartax+1
- Swachh Bharat Mission: Open Defecation Free status achieved across rural areaspmfias
Healthcare Protection
- Ayushman Bharat: 410 million health cards providing ₹5 lakh annual coverage for vulnerable familiesindianarrative+1
The Digital Revolution: Technology as the Great Equalizer
Perhaps no factor has been more transformative in breaking poverty chains than India’s digital revolution. The JAM Trinity (Jan Dhan-Aadhaar-Mobile) has created an unprecedented platform for direct service delivery, eliminating intermediaries and ensuring benefits reach intended recipients.
Digital Poverty-Breaking Initiatives:
JAM Trinity Impact
- 1.35 billion Aadhaar enrollments providing universal digital identity
- 550 million Jan Dhan accounts enabling financial inclusion
- Mobile penetration is reaching rural areas with smartphone adoption
UPI Revolution
According to the UN General Assembly President Dennis Francis, India has “lifted 800 million people out of poverty simply by smartphone use” over the last 5-6 years. Rural farmers who never had banking relationships can now:manufacturing.economictimes.indiatimes
- Pay bills digitally
- Receive payments for agricultural produce
- Access credit through digital platforms
- Transfer money instantaneously
Direct Benefit Transfer Success
The DBT system has revolutionized welfare delivery by:
- Eliminating corruption and leakages
- Ensuring timely transfers to beneficiaries
- Reducing administrative costs
- Enabling real-time monitoring of scheme implementation
Women: The Unstoppable Force Breaking Poverty Chains
Women’s empowerment has emerged as the most powerful catalyst for poverty reduction in India. When women are economically empowered, entire families escape poverty with multiplier effects extending to communities.
Women-Led Poverty Reduction:
Self-Help Group Revolution
- 400 million women covered through SHG networks across India indianarrative+1
- Primary livelihood source for rural women
- Access to credit, savings, and insurance through formal channels
- Community institution building at the grassroots level
Lakhpati Didi Initiative
The ambitious Lakhpati Didi Scheme targets 2 crore women to achieve annual savings of ₹1 lakh or more. This initiative recognizes that women’s economic empowerment is central to household poverty eradication.pwonlyias+1
Digital Empowerment
- Digital Didis program providing technology skills to rural women journal.iujharkhand
- Smartphone usage enables access to markets and financial services
- E-commerce participation is creating new income opportunities
Economic Impact Potential
According to the McKinsey Global Institute, advancing women’s equality in India could add $770 billion to GDP by 2025. If women’s workforce participation increases from the current 25% to 50%, India could achieve 8% GDP growth.hindustantimes+1
Women-Focused Schemes Creating Impact:
- Ujjwala Yojana: Free LPG connections improving health and reducing drudgery
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana: Financial security for girl children
- Stand Up India: Business loans for women entrepreneurs
- TREAD Scheme: Government grants for women’s enterprises cleartax
Rural Transformation: Where the Battle Was Won
The most dramatic poverty reduction has occurred in rural India, where 81.1% of poverty has been eliminated since 2011-12. This transformation reflects a fundamental shift in rural economic opportunities and living standards.
Rural Poverty Breaking Factors:
Infrastructure Revolution
- Enhanced physical infrastructure improving rural mobility and connectivity
- Digital connectivity through BharatNet is bringing high-speed internet to villages
- Road connectivity via Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana is reducing isolation
Agricultural Transformation
- PM Kisan scheme provides direct income support to farmers
- Crop insurance protects against weather-related losses
- Market access improvement through e-NAM and FPO formation
- Allied sector development in dairy, fisheries, and horticulture
Employment Diversification
- MGNREGA provides employment security during the agricultural off-seasons
- Rural entrepreneurship through SVEP and other livelihood programs
- Skill development aligned with local economic opportunities
Consumption Pattern Changes
The rural-urban consumption gap has narrowed from 88.2% in 2009-10 to 69.7% in 2023-24. This convergence indicates:ndtv+1
- Improved purchasing power in rural areas
- Better access to goods and services
- Lifestyle improvements bridging traditional divides
Multidimensional Success: Beyond Income Poverty
India’s approach recognizes that poverty is multidimensional, encompassing health, education, and living standards beyond just income. The National Multidimensional Poverty Index shows 24.82 crore people escaped multidimensional poverty in just nine years.pib+1
Multidimensional Poverty Reduction by State:
- Uttar Pradesh: 5.94 crore people
- Bihar: 3.77 crore people
- Madhya Pradesh: 2.30 crore people
- Rajasthan: 1.87 crore people
Key Improvements Across Dimensions:
- Nutrition: Malnutrition rates declined significantly
- Education: School enrollment and completion rates improved
- Housing: Access to pucca housing increased dramatically
- Sanitation: Open defecation has been eliminated in most areas
- Drinking Water: Tap water connections expanded through the Jal Jeevan Mission
- Electricity: Universal electrification achieved
- Financial Inclusion: Bank account ownership became universal
The Global Recognition and Lessons
India’s poverty reduction success has gained international acclaim. The UN General Assembly President specifically highlighted India’s achievement, noting that technological innovation enabled 800 million people to escape poverty. manufacturing.economictimes.indiatimes
Global Significance:
- Fastest large-country poverty reduction in modern history
- Technology-enabled delivery is becoming a global model
- Women-centric approach showing universal applicability
- Multidimensional framework offering comprehensive solutions
Lessons for Global Application:
- Political commitment at the highest level is essential
- Technology integration can dramatically improve efficiency
- Women empowerment creates maximum impact
- Comprehensive approach addressing multiple deprivations simultaneously
- State-specific strategies are necessary for diverse contexts
Current Challenges and Future Roadmap
Despite remarkable progress, challenges remain in completely eliminating poverty by 2030:
Persistent Challenges
- Climate change impact on rural livelihoods
- Employment quality and skill-market alignment
- Regional disparities require targeted interventions
- Urban poverty in growing metropolitan areas
- Informal sector coverage and social protection
Future Strategies
- Green jobs creation for climate-resilient livelihoods
- Advanced skill development for Industry 4.0
- Universal Basic Income pilot programs
- Climate adaptation support for vulnerable communities
- Technology upgradation for continued digital inclusion
Poverty in India: Breaking the Chains- The Road Ahead
India’s poverty reduction journey represents breaking multiple chains simultaneously:
- Economic chains: Through financial inclusion and employment
- Social chains: Via education and healthcare access
- Gender chains: Through women’s empowerment
- Digital chains: By bridging the technology divide
- Geographic chains: Connecting rural areas to opportunities
The 2030 Vision:
- Complete extreme poverty elimination
- Universal healthcare coverage
- Full employment generation
- Climate-resilient livelihoods
- Gender equality achievement
Conclusion: A Global Success Story
India’s journey from having 270 million extremely poor people to achieving near-elimination of extreme poverty in just over a decade stands as one of humanity’s greatest achievements. The combination of political will, technological innovation, comprehensive social protection, and women’s empowerment has created a replicable model for global poverty eradication.
The chains of poverty that bound millions of Indians have been systematically broken through:
- Targeted government interventions reaching the last mile
- Digital revolution enabling transparent service delivery
- Women’s economic empowerment creates multiplier effects
- Comprehensive social safety nets protecting vulnerable populations
- State-level innovations adapted to local contexts
As India moves toward its 2047 Viksit Bharat vision, the poverty reduction success provides a strong foundation for achieving developed nation status. The lessons learned and systems created offer hope not just for India’s remaining poor, but for the global fight against poverty.
The transformation from being home to the world’s largest number of poor people to becoming a global model for poverty reduction demonstrates that with the right approach, even the most entrenched social challenges can be overcome. India has not just broken the chains of poverty—it has shown the world how to do it at scale.
- https://visionias.in/current-affairs/upsc-daily-news-summary/article/2025-06-27/the-indian-express/economics-indian-economy/the-truth-about-poverty-in-india
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Poverty_in_India
- https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2124545
- https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/indias-rural-poverty-down-to-4-86-from-25-7-in-12-years-sbi-report-7391871
- https://www.financialexpress.com/policy/economy-poverty-below-5-per-cent-urban-rural-gap-reducing-sbi-research-3706894/
- https://vajiramandravi.com/current-affairs/unmasking-poverty-in-india-what-the-world-bank-data-really-tells-us/
- https://www.developmentaid.org/news-stream/post/196319/has-india-actually-turned-the-tide-on-poverty
- https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1996271
- https://www.drishtiias.com/daily-updates/daily-news-analysis/multidimensional-poverty-index-niti-ayog-1
- https://www.pmfias.com/poverty-reduction-in-india/
- https://www.indianarrative.com/opinion/269-million-stories-of-change-inside-indias-poverty-alleviation-miracle/
- https://ecoholics.in/poverty-eradication-programmes/
- https://www.theeconomicsjournal.com/article/view/248/6-2-1
- https://www.ispp.org.in/public-policy-for-poverty-reduction-and-growth/
- https://www.drishtiias.com/daily-updates/daily-news-editorials/tackling-poverty-a-multi-dimensional-challenge
- https://pwonlyias.com/women-empowerment-schemes/
- https://cleartax.in/s/women-empowerment-schemes-in-india
- https://manufacturing.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/hi-tech/india-lifted-800-million-people-out-of-poverty-simply-by-smartphone-unga-president/112210714
- https://www.hindustantimes.com/ht-insight/gender-equality/womens-economic-empowerment-as-a-means-to-alleviate-poverty-101724076649223.html
- https://journal.iujharkhand.edu.in/June-2023/Digital-Initiatives-for-Empowering-Rural-Women.html
- https://www.mahilahousingtrust.org/women-empowerment-key-to-sustainable-development-in-india/
- https://www.pmfias.com/multidimensional-poverty-index/
- https://www.newindianexpress.com/web-only/2025/May/27/the-number-of-poor-are-falling-in-india-is-it-time-to-shift-the-poverty-line-now
- https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1948814
- https://india.generation.org/news/break-the-chain-bring-in-change/
- https://www.indiabudget.gov.in/budget_archive/es2004-05/chapt2005/chap103.pdf
- https://testbook.com/rbiblogs/the-impact-of-government-schemes-on-poverty-alleviation/
- https://www.niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2023-08/India-National-Multidimentional-Poverty-Index-2023.pdf
- https://www.newindianexpress.com/business/2025/Jan/03/rural-urban-poverty-ratios-plunge-to-486-409-in-fy24-from-255-137-in-fy12
- https://borgenproject.org/poverty-in-kerala/
- https://economictimes.com/news/economy/indicators/poverty-gap-shrinks-between-rural-and-urban-india-in-fy24-driven-by-higher-consumption-sbi-report/articleshow/116901912.cms
- https://www.smilefoundationindia.org/blog/role-of-budget-2025-in-advancing-women-empowerment-initiatives-in-india/
- https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/poverty-alleviation-and-employment-generation-programmes-in-india/122367758
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41599-024-02645-x
- https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/03ab2401-8266-4959-b6b5-c70a723c0bff/content
- https://www.pib.gov.in/PressNoteDetails.aspx?NoteId=151873&ModuleId=3
- https://www.internationaljournalssrg.org/IJHSS/2017/Volume4-Issue4/IJHSS-V4I4P101.pdf
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/fa94cf67bfc1a3228a1b618e736d71ef/29d44b03-2e06-46fe-8d11-93f2c85d3016/162ff1f8.csv
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/fa94cf67bfc1a3228a1b618e736d71ef/29d44b03-2e06-46fe-8d11-93f2c85d3016/a50d7616.csv
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/fa94cf67bfc1a3228a1b618e736d71ef/29d44b03-2e06-46fe-8d11-93f2c85d3016/3af83982.csv
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/fa94cf67bfc1a3228a1b618e736d71ef/29d44b03-2e06-46fe-8d11-93f2c85d3016/9a0383f8.csv
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/fa94cf67bfc1a3228a1b618e736d71ef/29d44b03-2e06-46fe-8d11-93f2c85d3016/0993fb87.csv