
Religious Tensions – India’s Fragile Harmony under threat
India stands at a critical juncture in 2025, where its foundational promise of secular democracy faces unprecedented challenges. The nation that once prided itself on “unity in diversity” now grapples with religious tensions that threaten to unravel the very fabric of its pluralistic society. With communal violence surging by 84% in 2024 and systematic targeting of religious minorities reaching alarming levels, India’s fragile harmony hangs in the balance.
This is not merely a story of isolated incidents or periodic flare-ups—it represents a fundamental shift in India’s social contract, where centuries of coexistence are being tested by the forces of religious nationalism, political opportunism, and institutional bias. The data reveal a disturbing reality: 49 out of 59 communal riots in 2024 occurred in BJP-ruled states, while religious minorities face unprecedented persecution through legal mechanisms, extrajudicial violence, and systematic discrimination.
The Numbers That Define a Crisis
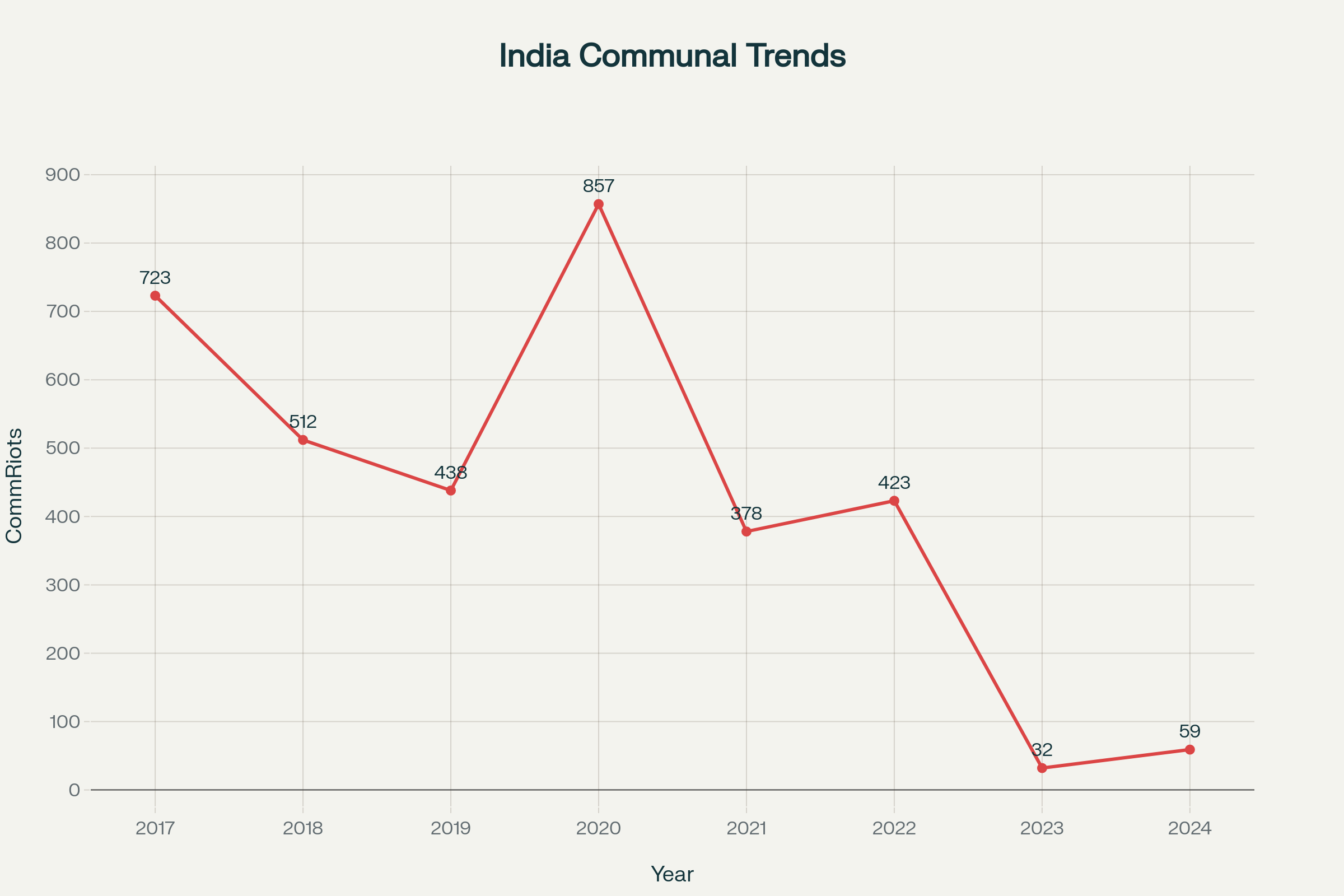
India’s Communal Violence Roller Coaster: 84% Spike in Religious Riots During 2024
India’s communal violence landscape has experienced dramatic fluctuations that reflect the volatile nature of religious tensions. The 2024 surge to 59 riots represents an 84% increase from the previous year’s 32 incidents, marking a concerning reversal of what appeared to be improving trends.opendoors+1
Communal Violence Trajectory (2017-2024):
| Year | Communal Riots | Deaths | Key Trigger Events |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 723 | 111 | Post-election tensions |
| 2018 | 512 | 160 | Ramnavami clashes |
| 2019 | 438 | 91 | CAA protests began |
| 2020 | 857 | 195 | Delhi anti-CAA riots |
| 2021 | 378 | 142 | Post-COVID tensions |
| 2022 | 423 | 178 | Ram Navami violence |
| 2023 | 32 | 25 | Relative calm |
| 2024 | 59 | 13 | Electoral polarization |
The 2020 peak of 857 riots, coinciding with the anti-Citizenship Amendment Act protests, marked a watershed moment, while the 2024 resurgence during election season reveals how political cycles amplify religious tensions. Most alarmingly, of the 13 deaths in 2024, 10 were Muslims, highlighting the disproportionate impact on minority communities.cnn
Targeting the Minorities: A Pattern of Persecution
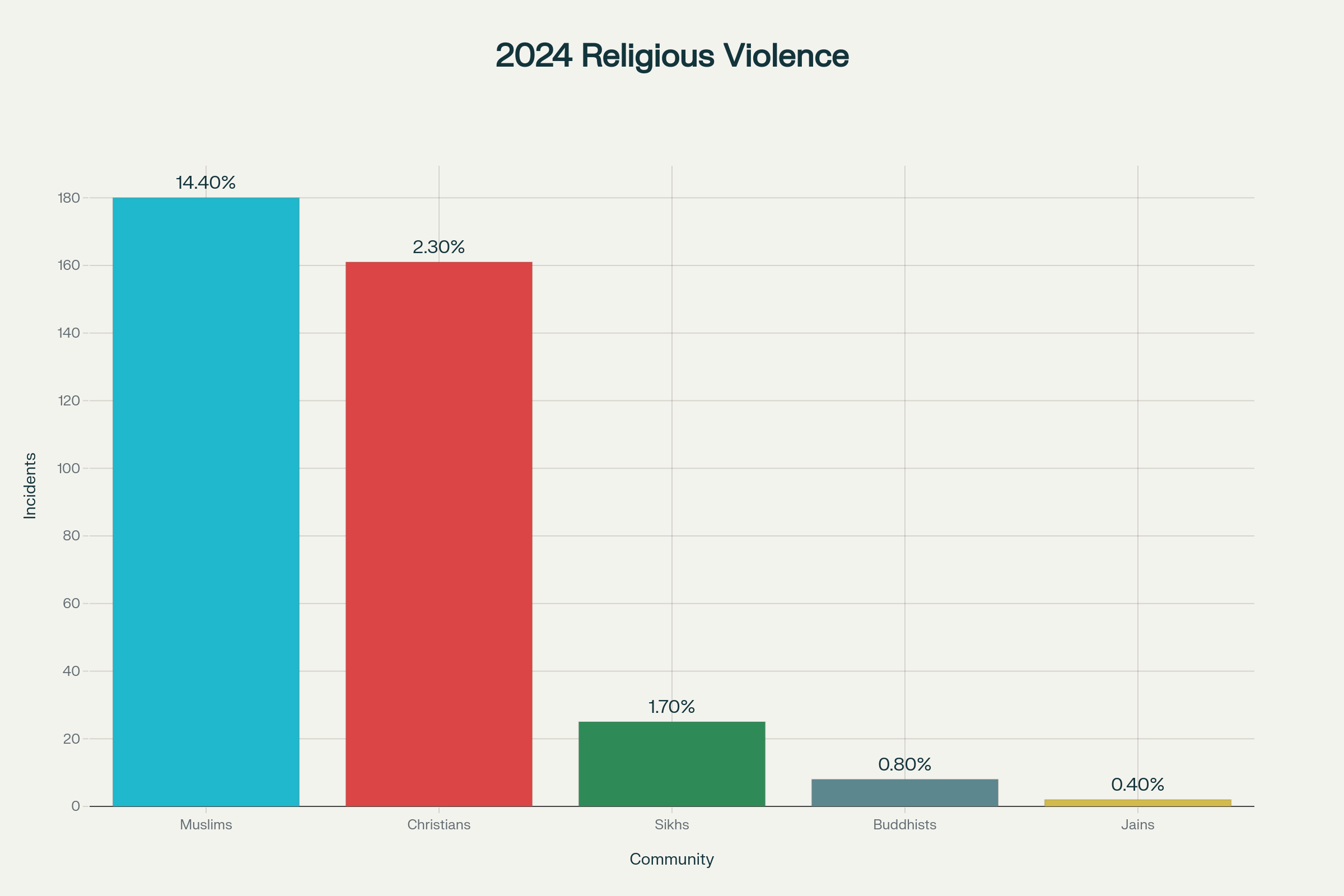
Targeting Minorities: Religious Violence Incidents by Community in 2024
The systematic nature of religious persecution in India becomes evident when examining violence against different communities. Despite representing smaller populations, Muslims and Christians bear the brunt of organized attacks, revealing a targeted campaign rather than random violence.
Religious Violence by Community (2024):
- Muslims (14.4% population): 180 violence incidents, 8 lynching deaths
- Christians (2.3% population): 161 violence incidents, 35 property demolitions
- Sikhs (1.7% population): 25 incidents
- Buddhists (0.8% population): 8 incidents
- Jains (0.4% population): 2 incidents
The disparity is stark: Christians face 70 times more violence per capita than their population share would suggest, while Muslims experience violence at 12.5 times their demographic proportion. This pattern indicates systematic targeting rather than isolated communal disputes.
State-Sponsored Persecution: The Bulldozer Phenomenon

Bulldozer justice: The new face of punitive state action targeting religious minorities
Perhaps no symbol better represents the institutionalization of religious persecution than the “bulldozer justice” phenomenon—where state authorities demolish properties belonging to accused individuals, primarily Muslims, without due process. Between 2022 and 2024, over 150,000 homes were demolished, displacing approximately 738,000 people.wikipedia+1
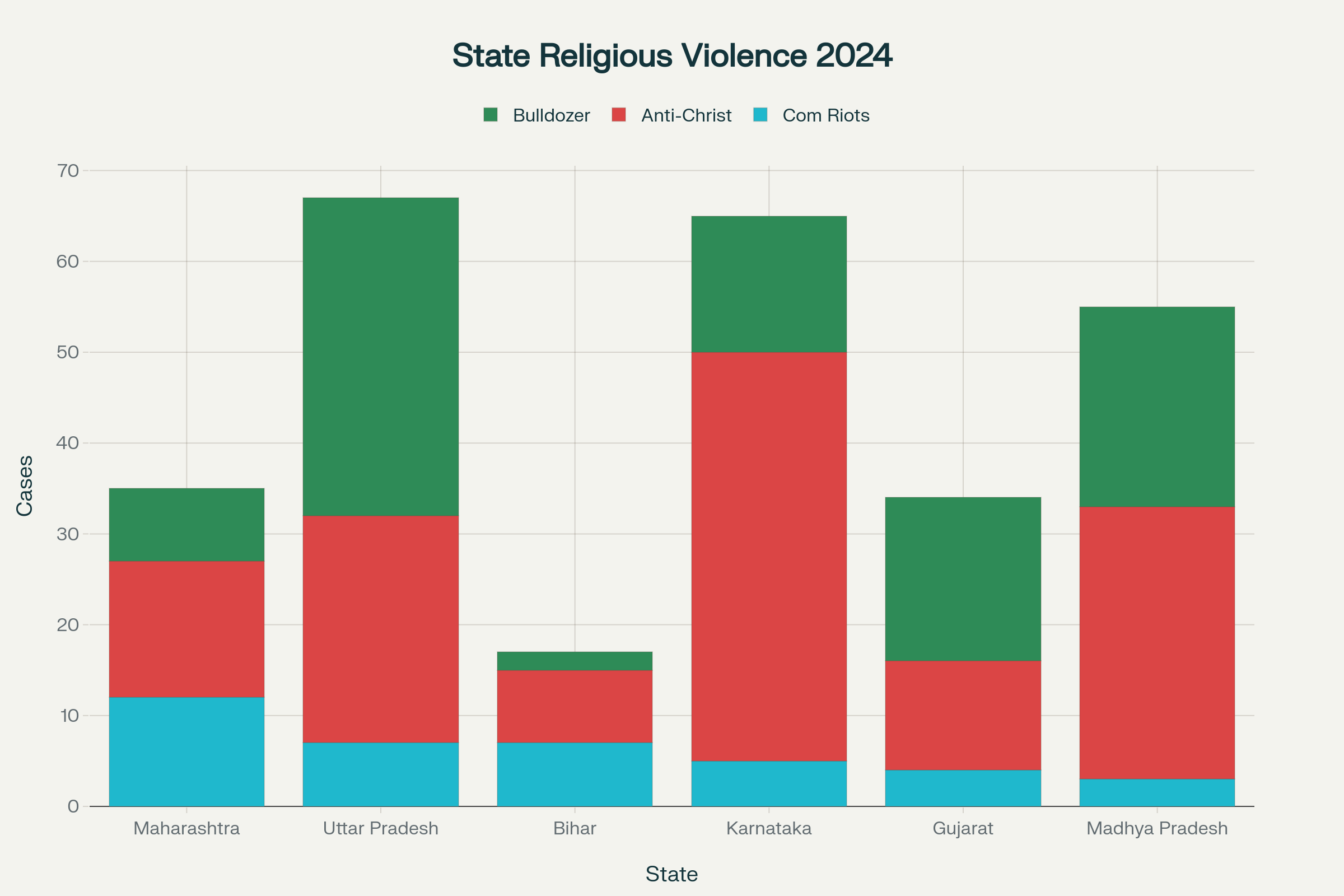
State-wise Religious Violence Breakdown: Maharashtra and UP Lead Multiple Categories
State-wise Analysis of Religious Violence (2024):
The concentration of different forms of persecution reveals coordinated state-level approaches:
- Maharashtra: 12 communal riots (electoral tensions)
- Uttar Pradesh: 35 bulldozer actions (punitive demolitions)
- Karnataka: 45 anti-Christian violence incidents
- Gujarat: 18 bulldozer actions (model replication)
Critical Pattern: 83% of communal riots (49 out of 59) occurred in BJP-ruled states, while non-BJP states like West Bengal (TMC) recorded only 1 bulldozer action compared to 35 in UP.opendoors+1
The Indian Supreme Court’s November 2024 ban on bulldozer justice came too late for thousands of families, but the ruling stated: “The chilling sight of a bulldozer demolishing a building reminds one of lawlessness where might was right”.scroll
The Manipur Catastrophe: Ethnic Cleansing in Plain Sight

Manipur ethnic crisis: Two years of violence between Meitei and Kuki-Zo communities
The ongoing Manipur ethnic violence represents India’s most severe contemporary religious-ethnic crisis. Since May 3, 2023, the conflict between the predominantly Hindu Meitei community and the largely Christian Kuki-Zo tribes has created a humanitarian disaster of staggering proportions.
Manipur Crisis by Numbers:
- 258 people killed (majority Kuki-Zo Christians)
- 60,000 internally displaced (creating refugee camps)
- 4,786 houses burned (systematic destruction)
- 386 religious structures destroyed (churches targeted)
- 663+ days of violence (no resolution in sight)
The viral video of two Kuki women being gang-raped and paraded naked in July 2023 shocked the nation, but police inaction for two months until the video emerged demonstrates systemic bias. The state’s effective partition into ethnic zones with buffer areas patrolled by central forces represents a failure of India’s federal system.cnn+1
International Implications: The resignation of Manipur’s BJP Chief Minister in February 2025 and imposition of President’s Rule indicate the central government’s recognition of complete administrative failure.cnn
Anti-Conversion Laws: Legislating Religious Freedom Away

Religious freedom under threat: Anti-conversion laws targeting minorities and interfaith relationships
The proliferation of anti-conversion laws across 12 Indian states represents a systematic assault on religious freedom, disguised as protection against forced conversions. These laws, primarily targeting Christians and Muslims, have created a legal framework for persecution.
Anti-Conversion Law Implementation:
| State | Year | Max Punishment | Cases Filed 2024 | Convictions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uttar Pradesh | 2020 | 10 years | 234 | 8 |
| Karnataka | 2022 | 10 years | 156 | 4 |
| Uttarakhand | 2018 | 3 years | 67 | 2 |
| Haryana | 2022 | 10 years | 45 | 1 |
| Jharkhand | 2017 | 3 years | 34 | 0 |
The conviction rate of less than 3% reveals these laws’ true purpose: harassment and intimidation rather than addressing genuine forced conversions. No state has produced evidence of systematic forced conversions, yet 847 cases were filed in 2024 alone.indianexpress+1
Impact on Christians: The European Centre for Law and Justice (ECLJ) recorded over 160 violent attacks against Christians in 2024, with nearly 600 religious services disrupted by Hindu extremists between January and September.indianexpress
Love Jihad: Criminalizing Interfaith Romance
The “love jihad” conspiracy theory—claiming Muslim men systematically seduce Hindu women for conversion—has been weaponized through legislation in multiple states. These laws require two-month waiting periods for interfaith marriages and criminalize interfaith relationships.
Interfaith Marriage Persecution (2024):
- Uttar Pradesh: 89 “love jihad” cases, 156 marriages stopped
- Karnataka: 67 cases, 89 marriages prevented
- Madhya Pradesh: 45 cases, 78 marriages blocked
- Haryana: 34 cases, 45 marriages stopped
The Dhanak support group reports that 1,000 interfaith couples seek help annually, with 52% Hindu women marrying Muslim men and 42% Muslim women marrying Hindu men—contradicting the “love jihad” narrative. Yet police routinely stop weddings, families face social ostracism, and couples require safe houses to survive.uscirf
Case Study: Sagar (Hindu) and Mohammed Shameem (Muslim) spent months in a Delhi safe house, attending multiple court hearings and police meetings where officials “scrutinized their marriage paperwork over and over again”. Their two-year journey to marry legally illustrates the systematic obstacles faced by interfaith couples.newsclick
The Hindu Nationalist Project: Redefining India
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) and its ideological parent, the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS), have systematically implemented a Hindu nationalist agenda that challenges India’s secular constitutional foundation. This project involves multiple dimensions:
Legislative Achievements
- Citizenship Amendment Act (2019): First religion-based citizenship law excluding Muslims
- Article 370 Abrogation (2019): Ending Kashmir’s special status
- Ram Mandir Construction (2024): Temple built on the demolished mosque site
- Triple Talaq Criminalization: Targeting Muslim Personal Law
Educational Saffronization
- NCERT textbook revisions: Minimizing Islamic contributions to Indian history
- Hindu astrology was introduced in university curricula
- Vedic education promoted over secular subjects
- Minority institution autonomy is undermined
Institutional Capture
- Supreme Court judges with RSS affiliations
- Police bias in communal violence investigations
- Administrative complicity in bulldozer justice
- Media polarization supporting majoritarian narratives
The International Dimension: Global Recognition of Crisis
India’s religious freedom crisis has attracted unprecedented international attention, damaging its global standing and aspirations for permanent UN Security Council membership.
United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF):
- Designated India as “Country of Particular Concern” (Tier-1 alongside China, North Korea)
- The 2024 report documented increasing abuses against religious minorities
- Noted “systematic, ongoing, and egregious” religious freedom violations ijssrr
Human Rights Watch (2024):
- Condemned the BJP government for “discriminatory and divisive policies”
- Documented “increased violence against minorities”
- Criticized “politically motivated criminal charges” against criticscsss-isla
European Parliament:
- Multiple resolutions condemning religious persecution
- Trade agreement discussions include religious freedom clauses
- Visa restrictions are considered for officials involved in persecution
United Nations:
- UN Human Rights Committee raised concerns about discrimination
- Special Rapporteurs investigating religious freedom violations
- Treaty body reviews highlighting systematic persecution hrw
Economic and Social Costs of Religious Polarization
Religious tensions extract enormous costs from India’s development trajectory:
Economic Impact
- Foreign investment hesitancy due to instability concerns
- Tourism decline in conflict-affected regions
- Brain drain as minorities seek opportunities abroad
- International isolation is affecting trade relationships
Social Fragmentation
- Educational segregation is increasing in mixed communities
- Residential ghettoization creates physical divisions
- Interfaith dialogue breakdown ending centuries of coexistence
- Youth radicalization through polarizing social media
Democratic Backsliding
- Press freedom erosion (India ranked 161/180 by RSF)
- Civil society crackdown using anti-terror laws
- Opposition persecution through investigative agencies
- Electoral manipulation using religious polarization
The Technology Factor: Digital Hate and Surveillance
Modern technology amplifies religious tensions through multiple mechanisms:
Social Media Weaponization
- WhatsApp lynch mobs organized through viral rumors
- Deepfake videos are creating false religious provocations
- Coordinated hashtag campaigns targeting minorities
- Algorithm bias amplifying inflammatory content
State Surveillance
- Aadhaar database enabling minority tracking
- Facial recognition at religious gatherings
- Phone intercepts of activists and journalists
- Digital arrests using cybercrime laws
Counter-Narratives
- Fact-checking initiatives combating misinformation
- Digital rights advocacy protecting minority voices
- International platforms bypassing domestic censorship
- Encryption tools enabling secure communication
Regional Variations: How Tensions Manifest Differently
Religious tensions take distinct forms across India’s diverse regions:
Hindi Belt (UP, Bihar, MP, Rajasthan)
- Cow vigilante violence targeting Muslim traders
- Love jihad prosecutions are preventing interfaith marriages
- Bulldozer justice as standard government response
- Madrasa closures are eliminating Islamic education
South India (Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, AP, Telangana)
- Anti-Christian violence in tribal areas
- Language politics intersecting with religious identity
- IT sector polarization is affecting workplace harmony
- Educational institutions targeting minority colleges
Northeast (Manipur, Assam, Nagaland, Mizoram)
- Ethnic-religious conflicts between indigenous groups
- Citizenship controversies affecting Bengali Muslims
- Church burning in tribal Christian areas
- Armed insurgency intersecting with religious identity
Western States (Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa)
- Industrial worker tensions in manufacturing cities
- Coastal smuggling blamed on Muslim communities
- Urban riots during religious festivals
- Business boycotts targeting minority entrepreneurs
The Role of Women in Religious Polarization
Women occupy a central position in India’s religious tensions, both as targets and agents of polarization:
Targeting Women
- Love jihad laws control female choice in marriage
- Rape as a weapon in communal violence (Manipur case)
- Honor killings for interfaith relationships
- Domestic violence justified through religious authority
Women as Mobilizers
- Hindu women’s organizations supporting majoritarian politics
- Religious education teaches children communal narratives
- Social media activism sis preading polarizing content
- Electoral participation is influenced by religious identity
Resistance and Agency
- Interfaith couples challenging legal restrictions
- Women’s rights activists opposing discriminatory laws
- Mother’s organizations seeking peace in conflict zones
- Professional women maintaining secular workspaces
Global Comparisons: Learning from Other Democracies
India’s religious polarization patterns mirror concerning global trends while maintaining unique characteristics:
Similar Patterns
- Myanmar: Buddhist majority targeting Rohingya Muslims
- Sri Lanka: Sinhala Buddhist nationalism vs. Tamil Hindus/Muslims
- Israel/Palestine: Religious-nationalist conflicts over territory
- United States: Christian nationalism challenging secular democracy
Distinctive Features
- Scale: India’s diversity makes polarization more complex
- Democracy: Unlike authoritarian systems, India maintains electoral competition
- History: Partition legacy creates unique Hindu-Muslim dynamics
- Federalism: State-level variation in religious tensions
International Lessons
- South Africa: Truth and Reconciliation Commission model
- Northern Ireland: Power-sharing arrangements
- Canada: Multiculturalism policies
- Germany: Constitutional protection for minorities
The Path Forward: Can India’s Harmony Be Restored?
Despite the alarming trends, several factors suggest potential for reversing religious polarization:
Constitutional Resilience
- Supreme Court interventions limiting government excess
- Constitutional provisions protecting minority rights
- Federal structure allowing state-level variation
- Civil society’s resistance to maintaining democratic values
Economic Imperatives
- Global integration requires social stability
- Demographic dividend needs inclusive growth
- Innovation economy valuing diversity
- International competitiveness demands harmony
Social Counter-Currents
- Inter-religious marriages continue despite obstacles
- Workplace integration in modern sectors
- Educational mixing in urban institutions
- Cultural synthesis in entertainment and the arts
Political Alternatives
- Opposition unity on secular platforms
- Regional parties resisting Hindu nationalism
- Youth alienation from polarizing politics
- Women’s movements challenging the patriarchal-religious nexus
Recommendations for Restoration
Immediate Actions
- Repeal anti-conversion laws in all states
- Ban bulldozer justice through Supreme Court enforcement
- Prosecute hate crimes with specialized courts
- Protect interfaith couples through safe houses and legal aid
Medium-term Reforms
- Constitutional amendment strengthening secularism
- Police reform removing communal bias
- Educational curriculum promoting pluralism
- Media regulation preventing hate speech
Long-term Vision
- Truth and reconciliation process for past violence
- Affirmative action for riot victims
- Inter-faith dialogue institutionalization
- International monitoring of religious freedom
Conclusion: The Choice Before India

India’s fragile religious harmony: Religious tensions between Hindu, Muslim, and Christian communities
India stands at a crossroads where two visions of its future compete: the inclusive democracy envisioned by its founders versus the Hindu rashtra (nation) promoted by religious nationalists. The statistics are unambiguous—religious tensions have intensified systematically, minorities face unprecedented persecution, and democratic institutions are being weaponized for majoritarian ends.
The 84% surge in communal violence during 2024, the two-year ethnic cleansing in Manipur, the systematic targeting of 22 crore minorities, and the criminalization of interfaith love represent more than isolated incidents. They constitute a comprehensive assault on India’s pluralistic foundations.
Yet India’s story is not predetermined. The nation that achieved independence through non-violent resistance, built the world’s largest democracy, and created space for all faiths to flourish possesses the institutional memory and cultural resources to reverse these trends.
The choice is stark: continue down the path of religious polarization that leads to social fragmentation, international isolation, and economic stagnation, or recommit to the constitutional values that made India a beacon of hope for the developing world.
Time is running short. Every bulldozer that demolishes a home, every law that criminalizes love, every riot that claims innocent lives, and every institution that abandons neutrality push India further from its founding promise. The fragile harmony that took centuries to build can be destroyed in decades—but it can also be restored by those who remember that India’s greatness lies not in religious homogeneity but in unity amidst diversity.
The battle for India’s soul has begun. The outcome will determine whether the world’s largest democracy becomes a cautionary tale of majoritarian excess or a redemptive story of pluralistic renewal. The choice belongs to every Indian—and the world is watching.
- https://www.opendoors.org/persecution/reports/India-Media_Advocacy_Dossier-ODI-2025.pdf
- https://www.newindianexpress.com/nation/2025/Jan/28/india-witnessed-84-rise-in-communal-riots-in-2024-report
- https://www.cnn.com/2025/03/18/india/india-curfew-hindu-muslim-tomb-intl-hnk
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Religious_violence_in_India
- https://scroll.in/latest/1078383/india-saw-84-rise-in-communal-riots-in-2024-report
- https://www.cnn.com/2024/04/30/india/india-elections-varanasi-hindu-muslim-tensions-intl-hnk-dst
- https://www.hrw.org/world-report/2025/country-chapters/india
- https://indianexpress.com/article/india/2900-communal-violence-cases-india-5-years-govt-8311709/
- https://acleddata.com/report/india-votes-2024-resurgent-hindu-nationalism-sets-stage-upcoming-elections-driving-communal
- https://www.uscirf.gov/countries/india
- https://www.newsclick.in/how-hate-spread-2024-report-communal-violence-india
- https://ijssrr.com/journal/article/view/2273
- https://csss-isla.com/secular-perspective/report-on-communal-violence-in-india-february-2024/
- https://www.hrw.org/news/2025/03/27/india-ethnic-clashes-restart-manipur
- https://theloop.ecpr.eu/bulldozer-justice-punitive-populism-in-india/
- https://eclj.org/religious-freedom/hrc/anti-conversion-laws–persecutions-of-christians-in-india—un-side-event?lng=en
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2023%E2%80%932025_Manipur_violence
- https://thecontrapuntal.com/the-spectacular-violence-of-indias-bulldozer-justice/
- https://www.opendoorsuk.org/news/latest-news/anti-conversion-laws-india/
- https://acleddata.com/infographic/political-violence-indias-manipur-state-2023-2025
- https://www.dw.com/en/whats-next-after-india-outlaws-bulldozer-justice/a-70809419
- https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/09646639241251613
- https://www.amnesty.org/en/latest/news/2025/05/authorities-should-urgently-rehabilitate-thousands-displaced-in-two-years-of-ethnic-violence-in-manipur/
- https://www.scobserver.in/journal/sc-hearings-on-bulldozer-justice-what-has-happened-so-far/
- https://thediplomat.com/2025/07/has-hindutva-peaked-in-india/
- https://www.npr.org/2021/10/10/1041105988/india-muslim-hindu-interfaith-wedding-conversion
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bharatiya_Janata_Party
- https://www.hrw.org/news/2024/01/11/india-increased-abuses-against-minorities-critics
- https://theconversation.com/indias-love-jihad-anti-conversion-laws-aim-to-further-oppress-minorities-and-its-working-166746
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hindutva
- https://www.uscirf.gov/sites/default/files/2024-10/2024%20India%20Country%20Update.pdf
- https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2020/12/4/india-police-stop-interfaith-marriage-citing-love-jihad-law
- https://www.dw.com/en/india-can-hindu-nationalists-reshape-the-constitution/a-73143290
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Violence_against_Christians_in_India
- https://www.npr.org/2021/09/13/1036792748/indias-love-jihad-laws-make-marriage-difficult-for-interfaith-couples
- https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-india-55158684
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/168660d184c3e96b75712098cb5a17cc/1c047d2c-eee9-49ea-bdf2-15e9e1b08d39/3bf86eaf.csv
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/168660d184c3e96b75712098cb5a17cc/1c047d2c-eee9-49ea-bdf2-15e9e1b08d39/481427a3.csv
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/168660d184c3e96b75712098cb5a17cc/1c047d2c-eee9-49ea-bdf2-15e9e1b08d39/60efcb90.csv
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/168660d184c3e96b75712098cb5a17cc/1c047d2c-eee9-49ea-bdf2-15e9e1b08d39/9040a46d.csv
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/168660d184c3e96b75712098cb5a17cc/1c047d2c-eee9-49ea-bdf2-15e9e1b08d39/c5f29a5d.csv
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/168660d184c3e96b75712098cb5a17cc/1c047d2c-eee9-49ea-bdf2-15e9e1b08d39/77bcc37c.csv
